
Learn Z Transform Table - Differential Equations and use these formulas to solve differential equation. Compute answers using Wolfram's breakthrough technology & knowledgebase, relied on by millions of students & professionals. For math, science, nutrition, history. Z-transform Table (2) L5.1 p498 E2.5 Signals & Linear Systems Lecture 15 Slide 12 Inverse z-transform As with other transforms, inverse z-transform is used to derive xn from Xz, and is formally defined as: Here the symbol indicates an integration in counterclockwise direction around a closed path in the complex z-plane (known as contour. Learn Z Transform Table - Differential Equations and use these formulas to solve differential equation. All Tutorials 111 video tutorials Circuits 101 10 video tutorials Intermediate Electronics 65 video tutorials Microcontroller Basics 21 video tutorials Light Emitting Diodes 14 video tutorials.
z-Transform
Sometimes one has the problem to make two samples comparable, i.e. to compare measured values of a sample with respect to their (relative) position in the distribution. An often used aid is the z-transform which converts the values of a sample into z-scores:
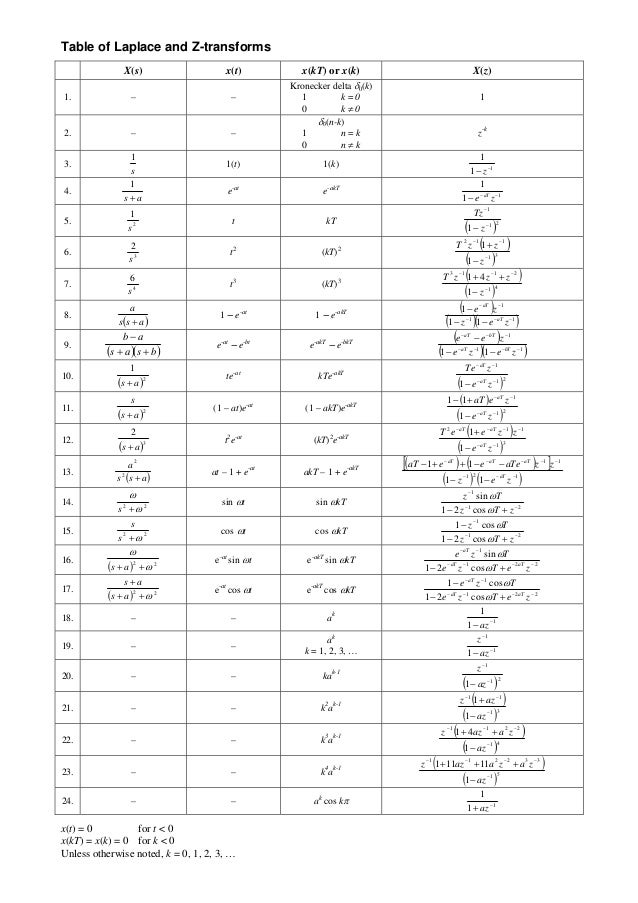
Z Transform Table Proof

with
zi ... z-transformed sample observations
xi ... original values of the sample
... sample mean
s ... standard deviation of the sample
The z-transform is also called standardization or auto-scaling. z-Scores become comparable by measuring the observations in multiples of the standard deviation of that sample. The mean of a z-transformed sample is always zero. If the original distribution is a normal one, the z-transformed data belong to a standard normal distribution (μ=0, s=1).
The following example demonstrates the effect of the standardization of the data. Assume we have two normal distributions, one with mean of 10.0 and a standard deviation of 30.0 (top left), the other with a mean of 200 and a standard deviation of 20.0 (top right). The standardization of both data sets results in comparable distributions since both z-transformed distributions have a mean of 0.0 and a standard deviation of 1.0 (bottom row).
Z Transform Tables Pdf
| Hint: | In some published papers you can read that the z-scores are normally distributed. This is wrong - the z-transform does not change the form of the distribution, it only adjusts the mean and the standard deviation. Pictorially speaking, the distribution is simply shifted along the x axis and expanded or compressed to achieve a zero mean and standard deviation of 1.0. |

z-Transform
Sometimes one has the problem to make two samples comparable, i.e. to compare measured values of a sample with respect to their (relative) position in the distribution. An often used aid is the z-transform which converts the values of a sample into z-scores:
with
zi ... z-transformed sample observations
xi ... original values of the sample
... sample mean
s ... standard deviation of the sample
The z-transform is also called standardization or auto-scaling. z-Scores become comparable by measuring the observations in multiples of the standard deviation of that sample. The mean of a z-transformed sample is always zero. If the original distribution is a normal one, the z-transformed data belong to a standard normal distribution (μ=0, s=1).
The following example demonstrates the effect of the standardization of the data. Assume we have two normal distributions, one with mean of 10.0 and a standard deviation of 30.0 (top left), the other with a mean of 200 and a standard deviation of 20.0 (top right). The standardization of both data sets results in comparable distributions since both z-transformed distributions have a mean of 0.0 and a standard deviation of 1.0 (bottom row).
Modified Z Transform Table
| Hint: | In some published papers you can read that the z-scores are normally distributed. This is wrong - the z-transform does not change the form of the distribution, it only adjusts the mean and the standard deviation. Pictorially speaking, the distribution is simply shifted along the x axis and expanded or compressed to achieve a zero mean and standard deviation of 1.0. |